

As systemd has a set of files, ensure to check the others like: This file is most likely located at /usr/lib/sysctl.d/nf. When using systemd and the systemd-coredump service, change the nf file.
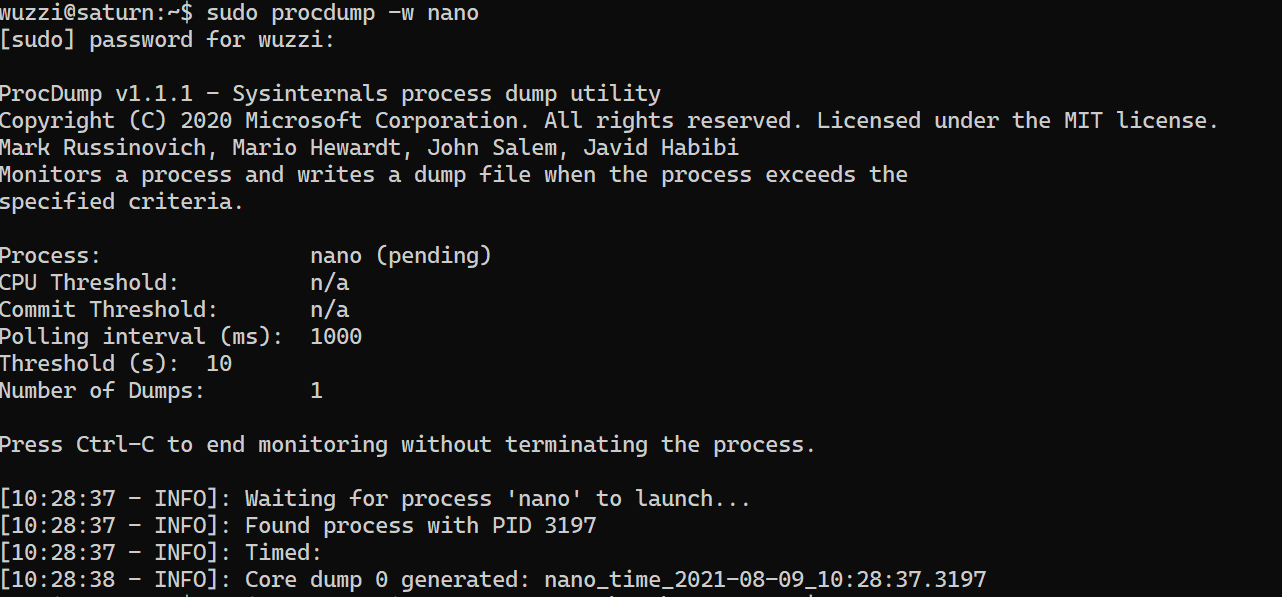
So choosing one of the options is the first step. Each user gets this value when logging in.īesides ulimit settings, there are also kernel settings to consider. This command adds the setting to a new file and sets both the soft and hard limit to zero. For example by creating a file named /etc/profile.d/disable-coredumps.sh.Įcho “ulimit -c 0 > /dev/null 2>&1” > /etc/profile.d/disable-coredumps.sh

The latter is preferred when it is available. The values for ulimit can also be set via /etc/profile or a custom file in the /etc/profile.d directory. The second column states if we want to use a hard or soft limit, followed by the columns stating the setting and the value. The asterisk sign means it applies to all users. Although it may look like a boolean (0 = False, 1 = True), it actually indicates the allowed size. If we would like to ensure that no process can create a core dump, we can set them both to zero. A hard limit is something that never can be overridden, while a soft limit might only be applicable for specific users. Good to know is that there are soft and hard limits. This is done via the /etc/security/nf file and defines some shell specific restrictions. To disable core dumps we need to set a ulimit value. Option 1: ulimit via the configuration file So if you don’t need the core dumps for troubleshooting purposes, disabling them is a safe option. This is because the files take up disk space and may contain sensitive data. It makes sense to disable any core dumps on Linux by default for all your systems. The second option is better suited for production systems storing or processing sensitive data. The first option is good for machines where unstable programs need to be investigated, like the workstation of a developer. On the other, we want to limit the debug data and avoid leaking sensitive data. On one hand, we want to gather data for improved stability and troubleshooting. As always, there is a tradeoff to make here. Most Linux systems have core dumps enabled by default. Disable setuid processes dumping their memory.Option 1: ulimit via the configuration file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
